
Leave a Message
We will call you back soon!
 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
 Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!
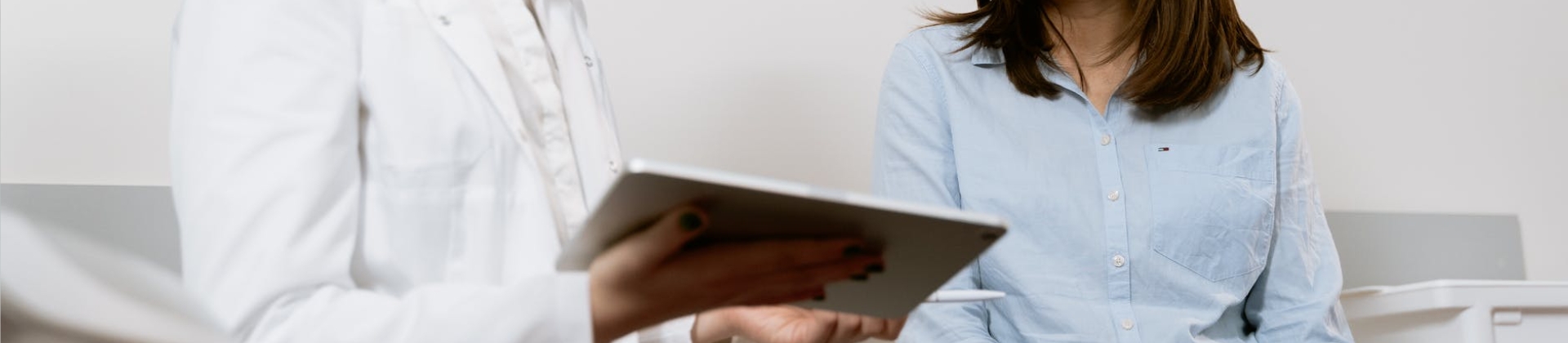

Peptide modifications refer to the chemical or enzymatic alterations performed on a peptide's amino acid sequence, to achieve various functional improvements, including increased solubility, enhanced stability, improved pharmacokinetics, enhanced selectivity and specificity, and many more. KS-V Peptide offers hundreds of peptide modifications to meet your research need. Our team of highly skilled scientists will choose the most suitable methods and techniques tailored to each project.
| 3-Mercaptopropyl (MPA) | D (+) Glucose | Lauric acid |
| 5-FAM | Dansyl | Lipoic acid |
| 5-FAM-Ahx | Dansyl-Ahx | Maleimide |
| Abz | Decanoic acid | 7-Methoxycoumarinyl-4-acetyl (MCA) |
| Acetylation | 2, 4-Dinitrophenyl (DNP) | Myristoyl |
| Acryl | DTPA | Octanoic acid |
| Alloc | Fatty Acid | OVA (-NH2 of N terminal) |
| Benzoyl | FITC | Palmytoyl |
| Benzyloxycarbonylation (CBZ) | FITC-Ahx | Pentinoic Acid |
| Biotin | Fmoc | Propiolic Acid |
| Biotin-Ahx | Formylation | Pyroglutamyl (pGlu) (Pyr) |
| Tertbutoxycarbonyl (Boc) | Hexanoic acid | Stearic acid |
| Br-Ac- | HYNIC | Succinylation |
| BSA (-NH2 of N terminal) | 4-Hydroxyphenylpropionic acid (HPP) | Thioester |
| Chenodeoxycholic acid | KLH (-NH2 of N terminal) | TMR |
| AFC | OtBu | Me |
| AMC | OBzl | NHEt |
| Amidation | EDA-Biotin | NHisopen |
| BSA (-COOH of C terminal) | Ethylamine | NHMe/NHEt |
| Bzl | Fuoro-methylketones (FMK) | OSU |
| Chloro-methylketones (CMK) | Hydrazine | OVA (-COOH of C terminal) |
| C-terminaleaters | KLH (-COOH of C terminal) | p-Nitroanilide (PNA) |
| Cysteamide | MAPS Asymmetric 2 branches | tBu |
| OMe | MAPS Asymmetric 4 branches | TBzl |
| OEt | MAPS Asymmetric 8 branches | Thioester |
Other modifications

Peptide modifications refer to the chemical or enzymatic alterations performed on a peptide's amino acid sequence, to achieve various functional improvements, including increased solubility, enhanced stability, improved pharmacokinetics, enhanced selectivity and specificity, and many more. KS-V Peptide offers hundreds of peptide modifications to meet your research need. Our team of highly skilled scientists will choose the most suitable methods and techniques tailored to each project.
| 3-Mercaptopropyl (MPA) | D (+) Glucose | Lauric acid |
| 5-FAM | Dansyl | Lipoic acid |
| 5-FAM-Ahx | Dansyl-Ahx | Maleimide |
| Abz | Decanoic acid | 7-Methoxycoumarinyl-4-acetyl (MCA) |
| Acetylation | 2, 4-Dinitrophenyl (DNP) | Myristoyl |
| Acryl | DTPA | Octanoic acid |
| Alloc | Fatty Acid | OVA (-NH2 of N terminal) |
| Benzoyl | FITC | Palmytoyl |
| Benzyloxycarbonylation (CBZ) | FITC-Ahx | Pentinoic Acid |
| Biotin | Fmoc | Propiolic Acid |
| Biotin-Ahx | Formylation | Pyroglutamyl (pGlu) (Pyr) |
| Tertbutoxycarbonyl (Boc) | Hexanoic acid | Stearic acid |
| Br-Ac- | HYNIC | Succinylation |
| BSA (-NH2 of N terminal) | 4-Hydroxyphenylpropionic acid (HPP) | Thioester |
| Chenodeoxycholic acid | KLH (-NH2 of N terminal) | TMR |
| AFC | OtBu | Me |
| AMC | OBzl | NHEt |
| Amidation | EDA-Biotin | NHisopen |
| BSA (-COOH of C terminal) | Ethylamine | NHMe/NHEt |
| Bzl | Fuoro-methylketones (FMK) | OSU |
| Chloro-methylketones (CMK) | Hydrazine | OVA (-COOH of C terminal) |
| C-terminaleaters | KLH (-COOH of C terminal) | p-Nitroanilide (PNA) |
| Cysteamide | MAPS Asymmetric 2 branches | tBu |
| OMe | MAPS Asymmetric 4 branches | TBzl |
| OEt | MAPS Asymmetric 8 branches | Thioester |
Other modifications